Launching a new website or a major update feels like a high-stakes premiere. All eyes are on you, and the last thing you want is a critical bug, a broken form, or a glaring typo stealing the show. While it's impossible to guarantee perfection, you can get remarkably close by systemizing your review process. This isn't about guesswork or frantic last-minute checks; it's about having a methodical, comprehensive plan that accounts for every potential point of failure.
A structured approach transforms a potentially chaotic launch into a controlled, predictable event. By following a detailed website quality assurance checklist, you can systematically identify and fix issues before they ever reach your audience. This process ensures your site delivers on its core promises, from functionality to user experience, safeguarding your brand's reputation and maximizing its impact from the moment it goes live.
This definitive guide breaks down the entire quality assurance process into eight manageable, yet crucial, stages. We will cover everything you need to build a professional, reliable, and high-performing website. You will learn how to validate:
- Cross-Browser Compatibility to ensure a consistent experience for all users.
- Mobile Responsiveness for flawless performance on any device.
- Page Load Speed to prevent user frustration and improve search rankings.
- Security Vulnerabilities to protect your site and user data.
- Content and SEO to maximize visibility and engagement.
- User Experience (UX) for intuitive navigation and clear calls-to-action.
- Core Functionality to confirm every link, form, and feature works as intended.
- Accessibility Compliance to make your site usable for everyone.
Think of this as your pre-launch flight check. Each step is designed to ensure your website not only works but excels from day one, delivering an exceptional experience for every visitor.
1. Cross-Browser Compatibility Testing
A core component of any thorough website quality assurance checklist is ensuring your site delivers a consistent, functional, and visually appealing experience to every visitor, regardless of how they access it. Cross-browser compatibility testing is the systematic process of verifying that your website works as intended across a wide range of web browsers, their different versions, and the operating systems they run on. It’s about ensuring that everything from CSS styling and JavaScript functionality to form submissions and media playback is uniform and reliable.
Without this crucial step, a feature that works perfectly in Google Chrome might be completely broken in Safari or display incorrectly in Microsoft Edge. This inconsistency can lead to a frustrating user experience, higher bounce rates, and a loss of potential conversions, undermining all the hard work put into your site's design and development.

Why It's a QA Priority
Imagine an e-commerce checkout button that is unclickable for all Firefox users or a critical navigation menu that fails to render on mobile Safari. These are not just minor glitches; they are direct barriers to business. For example, major platforms like Netflix must guarantee that video streaming is seamless on every major browser to retain subscribers. Similarly, banking websites must ensure their security protocols and transaction forms function flawlessly, even on older enterprise browsers still used by corporate clients.
Key Insight: The goal isn't to make your website look pixel-perfect and identical in every browser. Instead, it's about providing a comparably excellent and functional experience for all users, embracing a strategy of progressive enhancement where modern browsers get the full experience while older ones receive a solid, usable baseline.
How to Implement Cross-Browser Testing
Effectively tackling this part of the QA process requires a strategic approach. It's impractical to test every single browser version ever released, so prioritization is key.
- Prioritize Based on Data: Use analytics tools (like Google Analytics) to identify the top browsers and devices your audience uses. Focus your primary testing efforts on the top 3-5 browsers that drive the most traffic to your site.
- Leverage Testing Tools: Manually testing on dozens of device-browser combinations is inefficient. Use platforms like BrowserStack or LambdaTest to automate screenshots and test live functionality across hundreds of real browsers and devices without needing a physical device lab.
- Combine Automated and Manual Testing: While automated tools are great for catching visual rendering bugs, manual testing is essential for verifying user flows, interactive elements, and overall usability on your most critical browser targets.
- Establish a Baseline: Test against the latest stable versions of major browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. Then, expand to include previous versions and mobile browsers based on your audience data. If you're facing persistent challenges, you can find valuable solutions by learning more about common cross-browser compatibility issues on divimode.com.
2. Mobile Responsiveness and Device Testing
With mobile devices now accounting for the majority of global web traffic, ensuring your website offers a flawless mobile experience is no longer optional; it's a fundamental requirement. Mobile responsiveness and device testing is a comprehensive QA process that verifies your site's ability to adapt seamlessly across a vast landscape of screen sizes, orientations, and device types, from the smallest smartphones to the largest tablets. It’s about guaranteeing that content reflows logically, touch interactions are intuitive, and performance remains fast on mobile networks.
A non-responsive website on a mobile device can be catastrophic for user engagement. Elements may appear broken, text can be unreadable without constant pinching and zooming, and navigation becomes a frustrating exercise. This poor experience directly translates to lost leads, abandoned carts, and a damaged brand reputation, making it a critical item on any website quality assurance checklist.
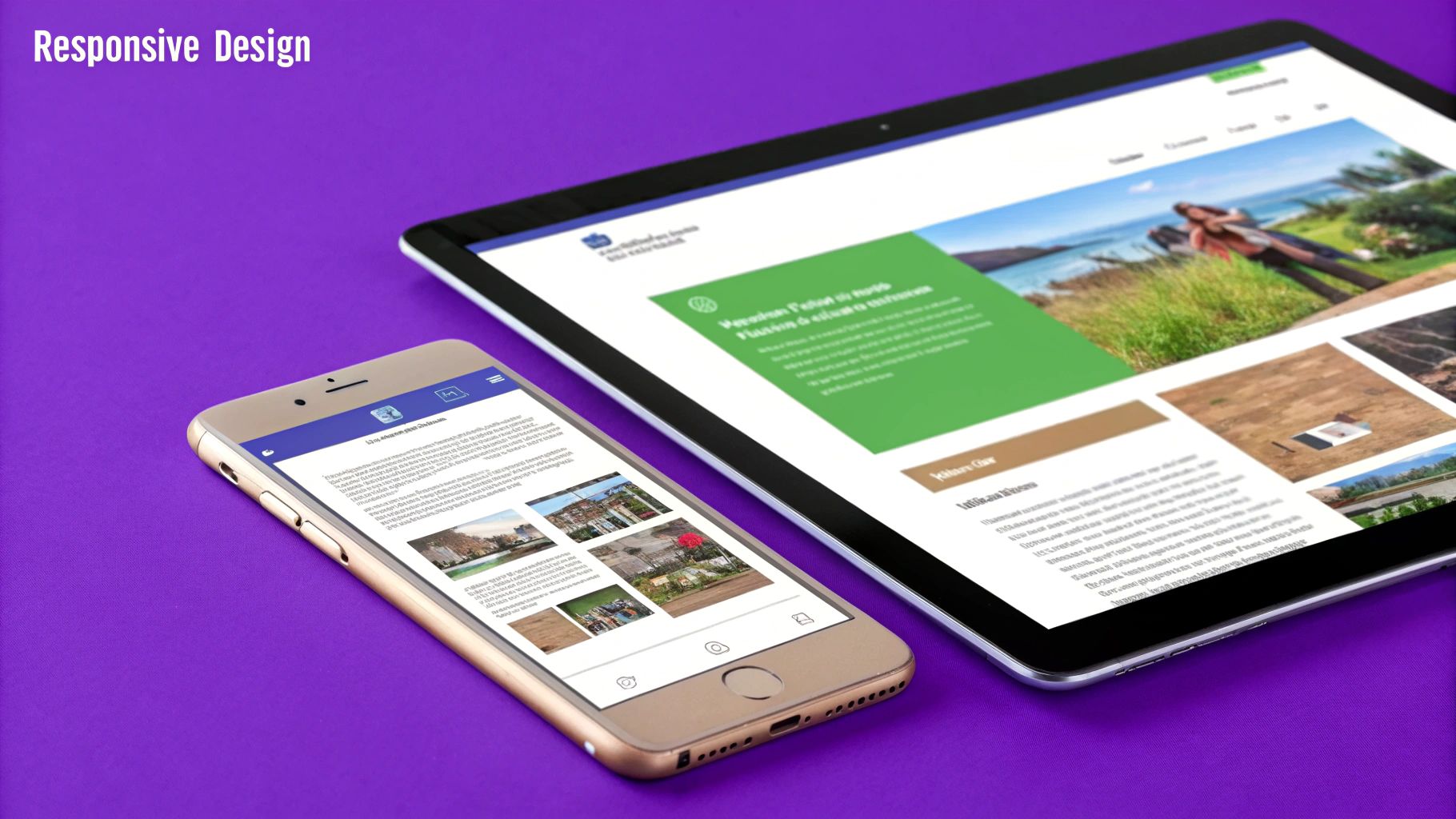
Why It's a QA Priority
Google's mobile-first indexing means the mobile version of your site is the baseline for how the search engine determines your rankings. A poor mobile experience doesn't just alienate users; it can severely harm your SEO visibility. For an e-commerce platform like Amazon, a responsive and optimized mobile checkout flow is directly tied to billions in revenue. Similarly, platforms like Airbnb rely on a seamless, responsive booking system that works flawlessly whether a user is on a desktop planning a trip or on their phone making a last-minute reservation.
Key Insight: True mobile responsiveness goes beyond just making a site fit on a smaller screen. It involves rethinking the user journey for a mobile context, prioritizing essential content, and optimizing every interaction for touch-based input and potentially slower network conditions.
How to Implement Mobile and Device Testing
An effective mobile QA strategy requires a multi-faceted approach that considers both the technical and user-experience aspects of mobile browsing.
- Adopt a Mobile-First Design: The most effective strategy is to design and develop for the smallest screen first and then progressively enhance the experience for larger screens. This forces a focus on core content and functionality from the outset.
- Test on Real Devices: While browser developer tools are excellent for initial checks, they cannot replicate the nuances of real-world device performance, touch sensitivity, or OS-specific quirks. It's crucial to test on a physical range of popular iOS and Android devices.
- Validate Key User Interactions: Manually test all interactive elements. Ensure buttons and links are large enough for easy tapping (a minimum of 44×44 pixels is a good practice). Verify that mobile forms are easy to complete, with appropriate keyboard types (e.g., a number pad for a phone number field).
- Check Both Orientations: Don't forget to test how your layout responds when a device is rotated from portrait to landscape mode. Content should reflow correctly without breaking the layout or hiding crucial information.
3. Performance and Page Load Speed Optimization
A critical pillar of any modern website quality assurance checklist is the systematic assessment of performance and page load speed. This process involves a deep analysis of all factors affecting how quickly your site loads and responds to user interaction. It covers everything from image compression and code minification to server response times and caching strategies, ensuring a swift and seamless experience that keeps users engaged.
In today's fast-paced digital environment, slow loading times are a direct cause of user frustration and abandonment. Even a one-second delay can drastically increase bounce rates and negatively impact conversions. A slow website is perceived as unprofessional and untrustworthy, directly harming your brand reputation and bottom line.

Why It's a QA Priority
Performance is not just a technical metric; it's a fundamental aspect of user experience and a proven driver of business success. For example, Walmart discovered a 2% increase in conversion rates for every one-second improvement in page load time. Similarly, the BBC found they lost an additional 10% of users for every extra second their site took to load. These figures demonstrate that speed is a feature and a direct contributor to revenue and user retention.
For Divi and WooCommerce users, performance is even more critical. A slow e-commerce site means abandoned carts, while a sluggish portfolio or business site fails to capture leads. Prioritizing speed ensures your design and functionality can deliver on their intended goals without being hindered by frustrating delays.
Key Insight: Website performance isn't a one-time fix; it's an ongoing commitment. The goal is to optimize the entire user journey, from the initial server request to the final pixel rendering on the screen, creating an experience that feels instantaneous and responsive.
How to Implement Performance Optimization
Integrating performance testing into your QA workflow requires a methodical approach focused on measurement, analysis, and targeted improvements.
- Benchmark with Core Web Vitals: Use tools like Google's PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, and WebPageTest to analyze your site's performance. Focus on key metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS).
- Optimize Your Assets: Compress all images using tools like TinyPNG and serve them in modern formats like WebP where supported. Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files to reduce their size by removing unnecessary characters without affecting functionality.
- Implement Smart Loading Strategies: Use lazy loading for images and videos below the fold, so they only load when a user scrolls to them. Prioritize the loading of critical CSS needed to render the above-the-fold content first to improve perceived load time.
- Leverage Caching and CDNs: Enable browser caching so repeat visitors can load the site faster. Implement a robust server-side caching solution (many WordPress plugins offer this). Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to distribute your assets across global servers, reducing latency for users far from your origin server.
4. Security Vulnerability Assessment
A critical, non-negotiable step in any website quality assurance checklist is a comprehensive security vulnerability assessment. This process involves systematically identifying, quantifying, and prioritizing vulnerabilities in your website's architecture and code. It goes far beyond simply installing a security plugin; it is a proactive defense strategy covering everything from SSL certificate validation and secure data transmission to protecting against common attacks like SQL injection, Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), and Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF).
Without a robust security assessment, your website becomes an open invitation for malicious actors. A single overlooked flaw can lead to data breaches, loss of customer trust, and severe financial and reputational damage. This QA step ensures that secure authentication mechanisms are in place and that the site complies with relevant security standards and data protection regulations.

Why It's a QA Priority
The consequences of security failures are catastrophic. The infamous Equifax breach, which cost the company over $4 billion, stemmed from a failure to patch a known software vulnerability. In contrast, platforms like PayPal and GitHub exemplify strong security posture. PayPal's robust multi-factor authentication system protects user accounts from unauthorized access, while GitHub's security-focused development practices and transparent vulnerability disclosure program build user trust and fortify its platform against emerging threats.
Key Insight: Website security is not a one-time task but an ongoing commitment. The goal is to create a multi-layered defense system where vulnerabilities are identified and remediated before they can be exploited, making security a foundational element of the development lifecycle, not an afterthought.
How to Implement a Security Assessment
Integrating security testing into your QA process requires a methodical and continuous effort. Prioritize threats based on potential impact to keep your protective measures effective and efficient.
- Scan and Test Regularly: Conduct automated vulnerability scans and periodic penetration testing to actively search for weaknesses. Tools from organizations like the OWASP Foundation can help identify common security risks.
- Deploy a Web Application Firewall (WAF): Implement a WAF, such as the one offered by Cloudflare, to filter and block malicious traffic before it ever reaches your server, providing a crucial layer of defense.
- Enforce HTTPS Everywhere: Ensure all traffic is encrypted by using a valid SSL certificate (services like Let's Encrypt offer them for free). This protects data in transit, not just on login or checkout pages. For a comprehensive approach to securing your website, consider reviewing a dedicated Cyber Security Audit Checklist to ensure all bases are covered.
- Maintain and Update Components: Regularly update all software, including your CMS, plugins, themes, and server dependencies. Unpatched software is one of the most common entry points for attackers. You can learn more about key practices to keep your Divi website safe on divimode.com.
5. Content Quality and SEO Optimization
Beyond functionality and design, the core substance of your website, its content, plays a pivotal role in user engagement and search engine visibility. This part of the website quality assurance checklist involves a meticulous audit of all on-page text, media, and metadata to ensure it is high-quality, relevant, and strategically optimized for search engines. It’s about verifying that every piece of content serves a purpose, answers user intent, and adheres to SEO best practices.
Failing to address content and SEO means even the most technically perfect website will struggle to attract organic traffic. Issues like duplicate content, poorly optimized meta tags, or irrelevant information can make your site invisible to search engines and unhelpful to users, effectively neutralizing your digital marketing efforts.
Why It's a QA Priority
Content is the primary vehicle for communicating value to both users and search engines. A QA process that neglects content quality misses the chance to build authority and drive conversions. For instance, HubSpot built its empire on a comprehensive blog strategy, generating millions of organic visitors by consistently publishing high-value, SEO-optimized content that addresses specific user pain points. Similarly, sites like Backlinko achieve top search rankings by creating data-driven, in-depth articles that become the definitive resource on a topic.
Key Insight: Modern SEO is not about stuffing keywords into thin content. It's about demonstrating expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness (E-A-T) by creating comprehensive content that genuinely satisfies user search intent and provides a superior experience.
How to Implement Content and SEO Audits
Integrating content and SEO checks into your QA workflow requires a systematic approach that blends analytical tools with strategic human review.
- Audit On-Page SEO Elements: Use tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs to crawl your site and check for critical SEO elements. Verify that every page has a unique, compelling title tag and meta description, a logical heading structure (one H1 per page), and optimized image alt text.
- Analyze Content for User Intent: Go beyond keywords and evaluate whether your content truly answers the questions your target audience is asking. If a user searches for “best running shoes for flat feet,” a top-ranking page should offer detailed comparisons and expert advice, not just a generic product list.
- Check for Uniqueness and Freshness: Use a tool like Copyscape to ensure your content is original and not duplicated across your site or from other sources. Identify important, evergreen content that needs regular updates to maintain its relevance and search ranking.
- Evaluate Internal Linking: A strong internal linking structure helps search engines understand your site's architecture and distributes link equity. Ensure that key pages are linked to from relevant contextual anchors within your blog posts, service pages, and other content.
6. User Experience (UX) and Usability Testing
Beyond pure functionality, a critical part of any website quality assurance checklist is evaluating how intuitive and satisfying the site is to use. User Experience (UX) and Usability Testing is the process of observing real users as they interact with your website to identify points of confusion, friction, and frustration. It focuses on ensuring navigation is logical, user flows are seamless, and the overall design feels effortless for your target audience.
A technically perfect website that is confusing or difficult to navigate will fail to retain users or drive conversions. This testing phase moves from "Can a user do this?" to "How easily and pleasantly can a user do this?" It uncovers the human element of your site's performance, providing insights that automated tests simply cannot capture.
Why It's a QA Priority
Poor usability directly impacts business goals. If users can't find the "add to cart" button, they won't buy. If the signup form is a frustrating maze, you lose potential leads. For instance, Airbnb's success is heavily tied to its relentless focus on a simplified booking process, which was refined through extensive user testing. Similarly, Dropbox’s intuitive file-sharing interface drastically reduced user confusion and became a key differentiator. These platforms demonstrate that a seamless user journey is a powerful competitive advantage.
Key Insight: Usability testing is not about asking users what they want; it’s about observing their behavior to see what they actually do. Users are often unable to articulate their pain points, but their actions will clearly reveal where your website's design is falling short.
How to Implement UX and Usability Testing
A systematic approach to UX testing ensures you gather actionable feedback to make meaningful improvements. It’s about creating a better experience, not just finding bugs.
- Test with Your Target Audience: Recruit 5-8 participants who represent your ideal customer profile. Testing with the right people provides far more relevant feedback than testing with a random group.
- Use Heatmap and Session Recording Tools: Tools like Hotjar or Crazy Egg visually show where users click, how far they scroll, and how they move through your site. This data is invaluable for identifying unexpected user behavior patterns and drop-off points.
- Conduct Task-Based Testing: Give users specific goals to accomplish (e.g., "Find a blue t-shirt and add it to your cart") and observe them without providing guidance. This reveals how intuitive your user flows truly are from different entry points.
- Prioritize Accessibility: Ensure your design adheres to Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). This not only serves users with disabilities but also improves the overall usability for everyone. You can learn more with a comprehensive website usability checklist on divimode.com.
7. Functional Testing and Feature Validation
The backbone of any reliable website quality assurance checklist is the rigorous confirmation that every feature does exactly what it's supposed to do. Functional testing is a systematic verification process that ensures all interactive components, from a simple contact form to a complex e-commerce checkout, operate flawlessly. This involves testing forms, search bars, user registration flows, interactive elements, and any custom-built functionality to guarantee they work correctly under all expected conditions and user interactions.
Without this validation, you risk launching a site with critical flaws. A broken “Add to Cart” button, a sign-up form that never submits, or a search feature that returns irrelevant results can directly halt the user journey. These functional failures are not just minor inconveniences; they are direct roadblocks to conversions, engagement, and user trust, rendering even the most beautiful design ineffective.
Why It's a QA Priority
Imagine an online learning platform where the "Enroll Now" button fails, or a SaaS application where a user cannot save their settings. These are catastrophic functional failures that destroy the core value proposition of the website. For example, a platform like Salesforce must conduct exhaustive functional testing on its CRM features to ensure data is correctly captured, updated, and displayed for different user roles. Similarly, Amazon's entire business model relies on a checkout process that has been tested against countless scenarios to ensure a smooth, error-free transaction every single time.
Key Insight: Functional testing isn't just about confirming success; it's equally about validating failure. A robust website should handle incorrect user inputs, server errors, and invalid actions gracefully, providing clear feedback to the user instead of simply breaking.
How to Implement Functional Testing
A structured approach is essential for covering all bases without getting overwhelmed. The goal is to create a repeatable process that validates every user-facing function.
- Create Detailed Test Cases: Document specific steps, expected outcomes, and actual results for every feature. A test case for a contact form might include scenarios for valid inputs, missing required fields, and incorrectly formatted email addresses.
- Test Both Positive and Negative Paths: Verify that the system works with correct data (positive testing) and that it properly handles invalid or unexpected data (negative testing). For instance, test what happens when a user enters letters into a phone number field.
- Test with Different User Roles: If your site has different access levels (e.g., admin, editor, customer), test each feature from the perspective of each role to ensure permissions are enforced correctly.
- Validate Data and API Integrity: After a form submission or an action, check that the data is correctly stored in the database. If your site uses APIs, test their requests, responses, and error-handling mechanisms thoroughly to ensure data is transmitted accurately.
8. Cross-Device and Accessibility Compliance Testing
An essential part of a modern website quality assurance checklist is ensuring your digital presence is inclusive and universally functional. Cross-device and accessibility compliance testing is the process of verifying that your website provides an equivalent and effective experience for all users, including those with disabilities, and works seamlessly across various devices and assistive technologies like screen readers. This goes beyond basic responsive design, focusing on true usability for everyone.
Failing to prioritize accessibility is not just a disservice to a significant portion of the population; it can also lead to legal challenges under regulations like the ADA and Section 508. A site that is difficult to navigate with a keyboard or impossible for a screen reader to interpret creates insurmountable barriers, excluding potential customers and damaging your brand's reputation.
Why It's a QA Priority
Imagine a visually impaired user trying to make a purchase on your e-commerce site, but the "Add to Cart" button has no descriptive text for their screen reader. Or consider a user with a motor impairment who relies solely on keyboard navigation but gets stuck in a "keyboard trap" on your contact form. These are not minor inconveniences; they are critical failures that prevent user engagement and transactions.
Major organizations like the BBC and Target have invested heavily in accessibility, not just for compliance but because it aligns with their core values and expands their audience reach. This commitment demonstrates that accessibility is a cornerstone of high-quality user experience, leading to a more robust and usable product for every single visitor.
Key Insight: Accessibility is not an add-on or a separate feature; it is a fundamental aspect of quality design and development. Building an accessible website from the ground up improves usability for all users, including those on mobile devices, with slow internet connections, or those with temporary impairments.
How to Implement Accessibility and Cross-Device Testing
A comprehensive approach combines automated tools with manual, human-centered verification. This ensures both technical compliance and real-world usability are addressed within your website quality assurance checklist.
- Start with Automated Scans: Use tools like WAVE or Deque’s axe DevTools as a first pass to automatically detect common accessibility issues, such as missing alt text, low color contrast, or incorrect ARIA roles.
- Conduct Manual Assistive Technology Testing: The most crucial step is to manually test with actual assistive technologies. Navigate your entire site using only a keyboard and then test key user flows with a screen reader (like NVDA, JAWS, or VoiceOver).
- Prioritize Semantic HTML: Ensure your code uses proper semantic markup (e.g.,
<nav>,<main>,<h1>,<button>). This provides a clear structure that assistive technologies rely on to interpret and present your content correctly. - Involve Users with Disabilities: The most effective way to understand if your site is truly accessible is to include users with disabilities in your testing process. Their firsthand feedback is invaluable for identifying genuine barriers that automated tools might miss.
Website QA Checklist Comparison
| Item | Implementation Complexity (🔄) | Resource Requirements (⚡) | Expected Outcomes (📊⭐) | Ideal Use Cases (💡) | Key Advantages (⭐) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-Browser Compatibility Testing | High – requires multiple environments and versions | High – needs testing infrastructure & tools | Ensures uniform functionality across browsers | Websites targeting diverse browser users | Increases accessibility and brand consistency |
| Mobile Responsiveness and Device Testing | High – numerous device/config tests needed | High – requires real devices and emulators | Seamless display on various devices | Mobile-first websites and apps | Captures mobile user base; boosts SEO and engagement |
| Performance and Page Load Speed Optimization | Medium – ongoing monitoring and optimizations | Medium – optimization tools and infrastructure | Faster loading times; better user experience | Sites needing speed for conversions and SEO | Improves search rankings; reduces bounce rates |
| Security Vulnerability Assessment | High – complex and specialized expertise required | High – skilled personnel and continuous updates | Protects data; prevents breaches | Websites handling sensitive data and transactions | Maintains trust; ensures compliance and legal safety |
| Content Quality and SEO Optimization | Medium – continuous content development and review | Medium – SEO tools and content teams | Increased organic traffic and user engagement | Content-heavy websites aiming for search visibility | Builds authority; improves user experience and traffic |
| User Experience (UX) and Usability Testing | High – time-intensive with user involvement | Medium to High – test users, analytic tools | Enhanced satisfaction and conversion rates | Sites focusing on usability and user-centered design | Reduces frustration; increases retention and loyalty |
| Functional Testing and Feature Validation | High – comprehensive, iterative test cases | Medium to High – automation tools and test envs | Reliable feature performance across scenarios | Complex, feature-rich websites and applications | Ensures data integrity; prevents feature failures |
| Cross-Device and Accessibility Compliance Testing | High – requires specialized knowledge and testing | Medium to High – assistive tech and expert testers | Legal compliance; widened audience reach | Websites targeting accessibility and device diversity | Demonstrates inclusivity; improves SEO and compliance |
From Checklist to Confidence: Your Next Steps
You've navigated the intricate landscape of website quality assurance, moving from the broad strokes of design to the granular details of security protocols. The comprehensive website quality assurance checklist detailed in this article is more than just a list of tasks; it's a strategic framework designed to transform your development process from reactive troubleshooting to proactive excellence. By systematically working through cross-browser compatibility, mobile responsiveness, performance optimization, security, content, user experience, functionality, and accessibility, you are building a digital asset engineered for success.
This process eliminates the guesswork and anxiety that often accompanies a website launch. Instead of crossing your fingers and hoping for the best, you are launching with the data-backed confidence that your site performs reliably across all user scenarios. This structured approach ensures every critical element, from the fastest-loading image to the most secure contact form, has been meticulously validated.
Key Takeaways: Shifting from Task to Mindset
The true value of this checklist lies in fostering a continuous improvement mindset. Quality assurance is not a final gate you pass through before launch; it is an ongoing commitment to delivering a superior user experience.
- Holistic Approach: True quality is achieved when all eight pillars work in harmony. A lightning-fast site (Performance) is useless if its forms are broken (Functionality), and a beautifully designed interface (UX) fails if it's inaccessible to users with disabilities (Accessibility).
- User-Centricity: Every item on this checklist ultimately serves the end-user. From ensuring content is error-free and SEO-optimized to guaranteeing the site works on their specific device, your goal is to create a seamless, trustworthy, and valuable experience.
- Proactive vs. Reactive: Integrating QA throughout the development lifecycle saves immense time, money, and reputational damage. It's far more efficient to catch a bug during development than to fix it after a public launch has been tarnished by a poor user experience.
For developers and agencies using the Divi framework, this foundational quality is the perfect launchpad for more advanced user engagement strategies. A solid, bug-free site earns user trust, making them more receptive to interactive elements like targeted offers, popups, and dynamic content.
Your Actionable Path Forward
Moving from theory to practice is the most critical step. Don't let this checklist become just another bookmarked article. Instead, put it into action immediately to solidify your processes and elevate the quality of your work.
- Customize and Adopt: Create a version of this website quality assurance checklist tailored to your specific project needs. Use a project management tool like Asana, Trello, or a simple spreadsheet to turn these points into a repeatable, actionable workflow for your team.
- Integrate Early and Often: Begin QA testing from the earliest stages of development. Test individual components as they are built rather than waiting to test the entire site at the end. This "shift-left" approach makes identifying and fixing issues significantly easier.
- Document Everything: Keep a detailed log of all tests performed, bugs found, and resolutions implemented. This documentation is invaluable for future updates, team member onboarding, and demonstrating your thoroughness to clients. It creates a historical record that helps identify recurring issues and improve your development process over time.
Remember, a meticulous quality assurance process is your ultimate competitive advantage. It’s what separates a good website from a great one, an amateur freelancer from a professional agency, and a one-time visitor from a loyal customer. By embracing this checklist, you are not just building websites; you are building trust, reliability, and a reputation for undeniable quality.
Once you've ensured your Divi website's core quality is impeccable, the next step is to enhance user engagement. Divimode's suite of tools, like Divi Areas Pro, allows you to create powerful, conditionally-triggered popups, fly-ins, and mega menus that captivate your audience. Turn your technically perfect site into a conversion machine by visiting Divimode to explore advanced user interaction possibilities.






